When it comes to concrete construction, the mix ratio is crucial in determining the strength and durability of the final product. In this article, we will go over the mix ratios for C20, C25, C30, C35, and C40 concrete, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of what each classification means and how it can be used in construction projects.
What is Concrete and How is it Classified?
Concrete is a composite material composed of water, cement, fine aggregates, and coarse aggregates. When mixed together, these ingredients form a paste that hardens over time, creating a durable and strong building material.
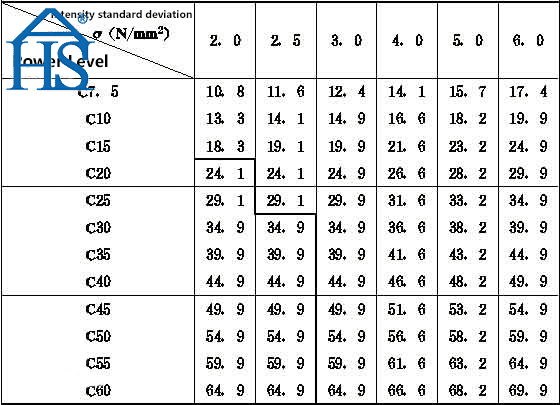
Concrete is classified based on its compressive strength, with each classification referring to the maximum amount of pressure that the concrete can withstand. The standard unit of measurement for concrete strength is Newtons per square millimeter (N/mm²).
The Mix Ratio for C20, C25, C30, C35, and C40 Concrete
Each classification of concrete is assigned a mix ratio, which specifies the proportions of the various ingredients needed to achieve that particular strength.
The mix ratios for C20, C25, C30, C35, and C40 concrete are as follows:
- C20: 1:2:4
- C25: 1:2:3
- C30: 1:1.5:3
- C35: 1:1:2
- C40: 1:1:1.5
The numbers represent the ratio of cement, fine aggregates, and coarse aggregates, respectively. For example, in C30 concrete, there is 1 part cement, 1.5 parts fine aggregates, and 3 parts coarse aggregates.
It’s important to note that the mix ratios listed above are general guidelines and may vary based on specific project requirements and the type of aggregates used.
The Importance of the Mix Ratio in Concrete Construction
The mix ratio is a crucial aspect of concrete construction because it directly affects the strength and durability of the final product. A higher mix ratio of cement and fine aggregates will result in a stronger concrete, while a lower mix ratio will result in a weaker concrete.
Additionally, the type of aggregates used in the mix can also impact the strength of the concrete. For example, using a larger proportion of coarse aggregates can result in a lower strength concrete, while using a larger proportion of fine aggregates can result in a stronger concrete.
How to Achieve the Ideal Mix Ratio for Your Concrete Project
In addition to understanding the mix ratios for C20, C25, C30, C35, and C40 concrete, it’s also important to know how to achieve the ideal mix ratio for your specific project requirements. Here are some tips to help you achieve the best possible mix ratio for your concrete project:
1. Use High-Quality Ingredients
Using high-quality ingredients is crucial in achieving the ideal mix ratio. Make sure to use cement that meets the relevant industry standards, as well as clean and well-graded aggregates. If possible, use fresh water for mixing the concrete to avoid introducing any impurities that could weaken the final product.
2. Measure Ingredients Accurately
Accurate measurement is key in achieving the ideal mix ratio. Make sure to measure the ingredients carefully and use a scale if possible. A small error in measurement can result in a significant difference in the final product.
3. Use a Concrete Mixer
A concrete mixer is a useful tool for achieving the ideal mix ratio. It ensures that the ingredients are mixed thoroughly, resulting in a homogeneous mixture that is less likely to contain any weak spots.
4. Follow the Mix Ratio Guidelines Carefully
Be sure to follow the mix ratio guidelines carefully, using the appropriate proportions of cement, fine aggregates, and coarse aggregates. If possible, perform a trial mix before starting your main project to ensure that the mix ratio is correct.
5. Monitor the Slump Test
The slump test is a simple test that measures the consistency of the concrete mixture. A well-mixed concrete should have a moderate slump, typically between 50 and 100 mm. Monitoring the slump test during the mixing process can help you to adjust the mix ratio as needed to achieve the desired consistency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the mix ratio for C20, C25, C30, C35, and C40 concrete is essential in determining the strength and durability of the final product in concrete construction projects. By following the general guidelines listed above, you can ensure that you are using the right mix ratio for your specific project requirements.
If you have any further questions or would like to discuss your concrete construction project in more detail, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We would be more than happy to assist you.
Email: sales@superior-abrasives.com
WhatsApp: +86-18638638803





